Quarterly highlights

Dr. C. Balakrishnan, Rheumatologist and DNB Teacher,
P D Hinduja Hospital, Mumbai
Landmark papers in Scleroderma: 2018
1. Cancer Risk and Systemic Sclerosis: New Insights.
a. Cancer risk was evaluated in subsets of scleroderma as made by serology and phenotype. Of more than 2000 patients, 205 had cancer. Those with anti-RNA III polymerase antibodies had a standardized incidence ratio of 2.8 and clinical phenotype informed cancer type. Diffuse scleroderma had a breast cancer risk, while limited had a lung cancer risk. Anti-centromere antibodies were protective. Thus autoantibodies and clinical features can be used for cancer risk stratification in scleroderma.
b. The presence of anti-RNAP III antibodies predicts cancer in SSc, but only 15% manifest malignancy. In the remaining 85%, serology is enriched with anti-RNAP I subunit antibodies. The presence of both antibodies together seems to protect against cancer. This was tested in a large cohort of 168 RNAPIII-positive patients, out of which 80 had cancer.
Igusa T, Hummers LK, Visvanathan K, Richardson C, Wigley FM, Casciola-Rosen L, Rosen A, Shah AA. Autoantibodies and scleroderma phenotype define subgroups at high-risk and low-risk for cancer. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Aug;77(8):1179-1186.
Shah AA, Laiho M, Rosen A, Casciola-Rosen L. Scleroderma patients with antibodies against the large subunits of both RNA polymerases-I and -III are protected against cancer. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 19. doi: 10.1002/art.40893.
2. The effect of smoking (ever or current) was evaluated on scleroderma outcomes; 3300 records were evaluated. Current smokers and ever-smokers had faster declines in FVC and lower baseline FVC and FEV1/FVC. Only heavy smoking (>25 pack years) accelerated digital ulcer development. There was no difference in mRSS severity. Thus the known adverse effect of smoking on bronchial airways and alveoli is also observed in SSc patients; however, the robust adverse effects of smoking on the progression of SSc‐specific pulmonary or cutaneous manifestations were not observed.
Jaeger VK, Valentini G, Hachulla E, Cozzi F, Distler O, Airó P, Czirják L, Allanore Y, Siegert E, Rosato E, Matucci-Cerinic M, Caimmi C, Henes J, Carreira PE, Smith V, Del Galdo F, Denton CP, Ullman S, De Langhe E, Riccieri V, Alegre-Sancho JJ, Rednic S, Müller-Ladner U, Walker UA; EUSTAR coauthors. Brief Report: Smoking in Systemic Sclerosis: A Longitudinal European Scleroderma Trials and Research Group Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;70(11):1829-1834.
3. Raynaud’s is common in patients with RNP positive disease, but the autoimmune nature of the same is irresolute. Antibodies derived from patient sera and from murine models of anti‐RNP autoimmunity were screened for the ability to induce RP‐like tissue ischemia and endothelial cell apoptosis in murine models. On proteomic analysis, cytokeratin 10 was identified as a candidate autoantigen. Monoclonal anti-K10 antibodies and K10 KO reproduced patterns of ischemic skin loss. Cold expression increased K10 expression. Thus these antibodies may show an autoimmune etiology to RP in RNP positive disease.
Ascherman DP, Zang Y, Fernandez I, Clark ES, Khan WN, Martinez L, Greidinger EL. An Autoimmune Basis for Raynaud's Phenomenon: Murine Model and Human Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Sep;70(9):1489-1499.
4. Lysophosphatidic acid has been shown to play a role in scleroderma pathogenesis. In a proof-of-concept study for an oral LPA1 receptor antagonist, 30 patients with a baseline mRSS of at least 15 were included. Headache, nausea, diarrhea, and falling were the most common side effects with an acceptable profile. A numerically greater but statistically insignificant reduction in mRSS (4.1 vs 3.5) at week 8 was noticed.
Allanore Y, Distler O, Jagerschmidt A, Illiano S, Ledein L, Boitier E, Agueusop I, Denton CP, Khanna D. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Antagonist SAR100842 for Patients With Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Eight-Week Placebo-Controlled Study Followed by a Sixteen-Week Open-Label Extension Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Oct;70(10):1634-1643.

Dr. Sanat Pathak, MD DM
Asst. Prof., Dept of Medicine,
BJ Government Medical College, Pune
Landmark Papers in Inflammatory Myositis: 2018
1. Introduction of a Novel Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Scoring System for Assessing Disease Activity in Children With Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Mandela ThyokaA novel MRI-based scoring system for reporting the severity of MRI findings in children with suspected JDM has been developed. Nine consultant pediatric radiologists independently assessed and scored 40 axial and 30 coronal thigh MR images of children with suspected JDM on two occasions using the juvenile dermatomyositis magnetic resonance imaging score (JIS). JIS was calculated for both reads for each plane and each limb, with possible scores ranging from 0 (normal) to 100 (severe). Inter- and intraobserver agreement was calculated using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and two- and one-way random effects models, respectively. Bland–Altman plots of the difference in JIS against the average JIS were also produced for each rater. Overall, the interobserver reliability and agreement was good. For axial images, the JIS ranged from 46.8 to 61.0 (ICC = 0.88 [95% CI: 0.82, 0.92]) for the left limb and 47.9–61.4 (ICC = 0.87 [95% CI: 0.81, 0.92]) for the right limb. For coronal images, JIS ranged from 56.7 to 65.1 (ICC = 0.90 [95% CI: 0.85, 0.95]) for the left limb and 55.7 to 66.8 (ICC = 0.90 [95% CI: 0.84, 0.94]) for the right limb. The intraobserver reliability and agreement was good, with ICC ranging from 0.90 to 0.94. Thus it is a semi-objective scoring system with the potential to serve as a reliable biomarker of disease severity and response to therapeutic interventions in children with JDM
Rheumatology, Volume 57, Issue 9, 1 September 2018, Pages 1661–1668, https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key144
2. The Performance of the European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Classification Criteria in an Expert-Defined 10-Year Incident Cohort
Matthew J SAdults with newly diagnosed IIM attending the Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust were identified over a 10-year period. A retrospective review of all putative cases was performed, and those fulfilling a consensus expert opinion diagnosis of IIM were included. Clinical, serological, and histological data were collected and each case was assigned a single IIM subtype. The EULAR/ACR classification criteria were then applied and sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were calculated, presented with 95% CIs. A total of 1637 cases were screened, with 255 consensus expert opinion IIM cases ultimately identified. Applying the EULAR/ACR classification criteria, the sensitivity to diagnose an IIM was 99.6% (95% CI 97.2, 100) and 80.9% (95% CI 76.0, 85.8) for the criteria cut-points of probable and definite diagnoses, respectively. In 94/255 cases, the IIM subtype differed between consensus expert opinion and classification criteria, most strikingly in the group subtyped as PM by the EULAR/ACR criteria, where there was a discrepancy in the majority (i.e. in 87/161). The EULAR/ACR criteria performed with high sensitivity in identifying IIM in this external cohort of incident IIM. However, substantial disagreements arose between consensus expert opinion and the criteria regarding IIM subtype assignments, resulting in a large proportion of criteria-assigned cases of PM having heterogeneous features. These results may have important implications for future use of these criteria in subsequent research.
Rheumatology, Volume 58, Issue 3, 1 March 2019, Pages 468–475, https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key343
3. Usefulness of Serum Krebs Von Den Lungen-6 for the Management of Myositis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
Satoshi TakanashiTo identify biomarkers for assessing myositis-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD), consecutive patients who had been newly diagnosed with PM, DM, or clinically amyopathic DM during the years 2002–2017 were reviewed. Patients were divided into two groups according to the presence of ILD, and the ILD group was further subdivided into three groups according to the clinical courses of induction failure, relapse, and non-relapse. Baseline and time-course changes in the parameters were compared between groups. Of the 110 patients enrolled, 75 (68%) had ILD. Baseline serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) was significantly higher in the ILD group than in the non-ILD group (1120 vs 236 U/ml; p<0.001). In the ILD group, consisting of the induction failure cases (n=3), the relapse group (n=24), and the non-relapse group (n=48), baseline serum KL-6 was significantly different between the three groups (1971 vs. 1870 vs. 935 U/mL, respectively; p=0.003 [relapse group vs. non-relapse group]). The time-course changes in serum KL-6 revealed that KL-6 significantly increased along with relapse, with the increase of 625 U/mL relevant to relapse and can be used as a useful biomarker for assessing the disease activity of myositis-associated ILD.
Rheumatology, key420, https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key420
4. Exacerbation of Murine Experimental Autoimmune Myositis by Toll‐Like Receptor 7/8
Clara ScioratiToll‐like receptor 7 (TLR‐7), TLR‐8, and interferon (IFN)–induced genes are expressed in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myositis. Experimental autoimmune myositis was induced in mice by injection of the amino‐terminal portion of the murine histidyl–transfer RNA synthetase (HisRS). Disease was compared in the presence or the absence of the TLR‐7/8 agonist R‐848 in wild‐type mice and in mice that fail to express the IFNα/β receptor (IFNα/βR‐null mice). Experimental autoimmune myositis induced by a single intramuscular immunization with HisRS spontaneously abated after 7–8 weeks. In contrast, levels of anti‐HisRS autoantibodies, endomysial/perimysial leukocyte infiltration, and myofiber regeneration persisted at the end of the follow‐up period (22 weeks after immunization) in mice immunized with HisRS in the presence of R‐848. Myofiber major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules were detectable only in mice immunized with both HisRS and R‐848. MHC up‐regulation occurred early and in muscles that were not directly injected with HisRS. Muscle MHC expression paralleled with leukocyte infiltration. MHC class I molecules were selectively up‐regulated in myotubes challenged with R‐848 in vitro. Type I IFN was necessary for prolonged autoantibody response and for the spreading of the autoimmune response, as demonstrated using IFNα/βR‐null mice. Muscle infiltration was maintained in the injected muscle up to the end of the follow‐up period. It was concluded that TLR‐7/8 activation is necessary to induce and maintain a systemic autoimmune response targeting the skeletal muscles. This experimental autoimmune myositis model reproduces many characteristics of human idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and may represent a tool for preclinical studies.
Arthritis Rheumatol, 70: 1276-1287. doi:10.1002/art.40503
5. Differential Clinical Associations of Anti–nuclear Matrix Protein-2 Autoantibodies in Patients With Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Hanbo Yang MDSerum levels of anti–NXP‐2 autoantibodies were determined in 709 patients with IIMs and also serially measured in patients’ sera with an in‐house enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay using MORC3 recombinant protein. Patients with anti–NXP‐2 autoantibodies were divided into 2 subgroups: those with and those without calcinosis. Associations between anti–NXP‐2 autoantibody levels and organ‐specific disease activity (using 10‐cm visual analog scale [VAS] scores), serum creatine kinase (CK) levels, and calcinosis severity were investigated in cross‐sectional and longitudinal analyses. A cross‐sectional analysis of 56 IIM patients with anti–NXP‐2 autoantibodies (38 without calcinosis and 18 with calcinosis) showed that in patients without calcinosis, the levels of anti–NXP‐2 autoantibodies were positively correlated with the physician's global assessment of disease activity and muscle VAS scores and serum CK levels, whereas no such association was found in patients with calcinosis. Results of the longitudinal study revealed strong correlations between anti–NXP‐2 antibody levels and the physician's global assessment and constitutional, cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and muscle VAS scores and serum CK levels in patients without calcinosis, but in patients with calcinosis, only a moderate correlation was observed between anti–NXP‐2 antibody levels and the physician's global VAS and constitutional VAS scores. Of note, in patients without calcinosis, anti–NXP‐2 autoantibodies were found to disappear during periods of clinical remission, but reappeared with disease relapse. No association between anti–NXP‐2 antibody levels and the severity of calcinosis was observed.
Arthritis Rheumatol, 70: 1288-1297. doi:10.1002/art.40491
6. Abatacept in the Treatment of Adult Dermatomyositis and Polymyositis: A Randomized, Phase IIb Treatment Delayed-Start Trial
Tjärnlund ATwenty patients with DM (n=9) or PM (n=11) with refractory disease were enrolled in a randomized treatment delayed-start trial to receive either immediate active treatment with intravenous abatacept or a three-month delayed-start. The primary endpoint was the number of responders, defined by the International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group definition of improvement (DOI), after six months of treatment. Secondary endpoints included the number of responders in the early treatment arm compared with the delayed treatment arm at three months. Repeated muscle biopsies were investigated for cellular markers and cytokines. Eight of 19 patients included in the analyses achieved the DOI at six months. At three months, five (50%) patients were responders after active treatment, but only one (11%) patient in the delayed treatment arm. Eight adverse events (AEs) were regarded as related to the drug: four mild and four moderate, and of the three serious AEs, none was related to the drug. There was a significant increase in regulatory T cells (Tregs), whereas other markers were unchanged in repeated muscle biopsies. In this pilot study, treatment of patients with DM and PM with abatacept resulted in lower disease activity in nearly half of the patients. In patients with repeat muscle biopsies, an increased frequency of Foxp3+ Tregs suggests a positive effect of treatment in muscle tissue.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2018;77:55-62.
7. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Infliximab in Refractory Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis
Adam SchiffenbauerA randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial including subjects with active DM or PM. Participants had stable doses of immunosuppressive medication and prednisone (≤0.5 mg/kg/day), and exhibited clinical signs of muscle weakness for at least four weeks prior to study entry. Participants received infusions of either placebo or infliximab 5 mg/kg at 0, 2, 6, and 14 weeks in a blinded manner. The primary outcome was a ≥15% manual muscle strength (MMT) improvement at week 16 compared to week 0. The secondary outcome measures were improvement defined by the International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) criteria. At week 16, responders in each arm had the option of either continuing the same treatment or changing to the non-responder treatment for that study arm. Non-responders in the 5 mg/kg infliximab arm were increased to infliximab 7.5 mg/kg for weeks 22, 30, and 38. Non-responders in the placebo arm at week 16 received infliximab 5 mg/kg at weeks 16, 18, 22, 30, and 38. Outcomes were reassessed at week 40. Twelve subjects completed the study to week 16. Six of the 12 subjects received infliximab treatment at the dose of 5 mg/kg, with only one subject meeting the responder criteria at that dose. Of the remaining five subjects on infliximab, three crossed over to the infliximab 7.5 mg/kg dose. One of those three subjects responded. All six patients in the placebo arm crossed over to the 5 mg/kg dosing regimen after week 16, and two of those responded to infliximab.
Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 47(6), 858–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2017.10.010

Dr. Nibha Jain, Specialist Registrar, Rheumatology,
University Hospital Leicester.
Landmark Papers in Lupus: 2018
1. Effectiveness of renoprotective approaches for persistent proteinuria in lupus nephritis: more than just immunosuppression. Castro M, Ugolini-Lopes M, Borba EF, Bonfá E, Seguro LPC. Lupus. 2018 Dec;27(14):2215-2219. doi: 10.1177/0961203318809883. Epub 2018 Nov 4.
Lupus nephritis is a major disease manifestation that leads to morbidity and mortality in SLE. Often, despite giving the best available immunosuppressive therapy, many patients continue to have persistent proteinuria. In a small study of thirteen patients with persistent proteinuria, anti-hypertensive drugs were optimized (targeting BP <130/80 by measuring BP every two weeks, and ensuring adherence to diet, therapy and avoiding smoking). After three months, there was a significant reduction in proteinuria (2.26 ± 1.09 vs. 0.88 ± 0.54 g/24 hours, p<0.001), mean prednisone dose (10.96 ± 6.73 vs. 5.38 ± 3.36 mg/day, p=0.013), and mean SLEDAI score (4.38 ± 0.72 vs. 3.08 ± 1.86, p=0.043). Although the sample size was small, this study emphasizes the need for controlling blood pressure before labeling refractory lupus nephritis, hiking dose, or changing immunosuppressive therapy.
2. A pivotal phase III, randomised, placebo-controlled study of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus located in China, Japan and South Korea. Zhang F, Bae SC, Bass D, Chu M, Egginton S, Gordon D, Roth DA, Zheng J, Tanaka Y. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Mar;77(3):355-363. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211631. Epub 2018 Jan 2.
Belimumab is a human, IgG1λ monoclonal antibody that binds soluble human BLyS and inhibits its activity. It has been approved by the FDA for use in SLE, based on two landmark trials, BLISS-52 and BLISS-76. However, these studies were conducted primarily in Europe and America. To assess the reproducibility of the effectiveness of belimumab in the Northeast Asian population, a phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study was conducted among 677 patients in China, Japan, and South Korea. At week 52, the primary endpoint, the SRI4 response rate, was higher with belimumab versus placebo (53.8% vs. 40.1%; OR: 1.99 [95% CI: 1.40, 2.82; p=0.0001]). In addition, the percentage of patients with a ≥4-point reduction in SELENA-SLEDAI and an SRI7 response was significantly greater for belimumab versus placebo. Patients using belimumab had a 50% lower risk of experiencing a severe flare (p=0.0004) and achieved a significantly greater reduction in the dose of steroids compared with placebo (p=0.0228). The incidence of AEs was similar between the placebo and belimumab groups. Despite results being in favor of belimumab, it is important to note that patients with active lupus nephritis and NPSLE were excluded from the study, similar to BLISS-52 and BLISS-76.
3. Efficacy and Safety of Atacicept in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results of a Twenty-Four-Week, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Arm, Phase IIb Study. Merrill JT, Wallace DJ, Wax S, Kao A, Fraser PA, Chang P, Isenberg D; ADDRESS II Investigators. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Feb;70(2):266-276. doi: 10.1002/art.40360. Erratum in: Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Mar;70(3):467.
Atacicept is a recombinant fusion protein that combines the binding site for two cytokines that regulate maturation, function, and survival of B cells - BLyS and A proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), with the constant region of immunoglobulin. In a 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm, phase IIb study (ADDRESS-II), the safety and efficacy of atacicept in SLE were assessed. In the intent-to-treat population of 306 patients, atacicept showed an acceptable safety profile, compared with placebo. The patients were randomized 1:1:1 to receive placebo, atacicept 75 mg, or atacicept 150 mg. At week 24, there was a trend toward an improved SRI-4 response rate (the primary endpoint) with atacicept 75 mg (57.8%; adjusted odds ratio [OR] 1.78, p=0.045) and 150 mg (53.8%; adjusted OR 1.56, p=0.121) as compared with placebo (44.0%). Sub-analysis showed a statistically significant improvement in patients with high disease activity and/or serologically active disease. These data suggest that although atacicept shows promise, further studies are required to establish the role of atacicept in the management of SLE.
4. Multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of bortezomib as a treatment for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Ishii T, Tanaka Y, Kawakami A, Saito K, Ichinose K, Fujii H, Shirota Y, Shirai T, Fujita Y, Watanabe R, Chiu SW, Yamaguchi T, Harigae H. Mod Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;28(6):986-992. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2018.1432331. Epub 2018 Feb 15
Abnormalities in B-cell tolerance are believed to play a central role in SLE pathogenesis. Therefore multiple strategies have been devised to target B cells, including rituximab and belimumab. However, plasma cells are resistant to traditional B-cell-depleting therapies and pose a therapeutic challenge in the management of refractory SLE. Bortezomib is a proteasome inhibitor that targets plasma cells and is approved for the management of multiple myeloma. It was presumed to have potential in overcoming this challenge of suppressing plasma cells and thus help manage refractory lupus patients. This notion was further supported by various case reports (Frolich K, et al., 2011 and de Groot KA et al., 2015) and an uncontrolled clinical trial (Alexander T, et al., 2015) in which successful outcomes were cited. In contrast, in a recent multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trial (n=14; bortezomib: placebo=2:1) from Japan, Ishii T et al. found that seven out of eight patients on bortezomib could not complete the trial due to adverse drug reactions. Larger studies directed at studying the safety and efficacy are required to establish whether such a high percentage of patients having adverse drug reactions was idiosyncratic, related to SLE, or related to racial characteristics.
Landmark Papers in Sjögren’s Syndrome: 2018
1. Epidermal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein: A Novel Marker in the Diagnosis of Dry Eye Disease in Sjögren Syndrome. Shinzawa M, Dogru M, Den S, Ichijima T, Higa K, Kojima T, Seta N, Nomura T, Tsubota K, Shimazaki J. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 4;19(11). pii: E3463. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113463. PMID: 30400384
Oxidative stress-related damage to lacrimal and salivary glands has been postulated to be one of the various contributory mechanisms for the characteristic sicca symptoms of Sjögren’s syndrome (SS). Fatty acid binding proteins (FABP) are a family of molecules that are expressed by various tissues in response to oxidative stress. Shinzawa et al. focused on the role of FABP5 (epidermal FABP), which is expressed in the oral mucosa, ocular surface, and exocrine glands, and tried to elucidate its potential as a novel biomarker in SS. They measured levels of E-FABP in serum, saliva, and tears of 11 new patients with untreated SS and 12 healthy control individuals. The E-FABP concentration in tears only showed significantly lower levels in patients with SS (mean, 323.5 ± 325.6 pg/mL) compared to healthy controls (mean, 4076 pg/mL; p=0.0136). The E-FABP concentration in tears significantly correlated with the results of dry eye parameters. Its usefulness is limited by the lack of standardization and facilities for tear collection.
2. Expression of interleukin-17 in primary Sjögren's syndrome and the correlation with disease severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Zhang LW, Zhou PR, Wei P, Cong X, Wu LL, Hua H. Scand J Immunol. 2018 Apr;87(4):e12649. doi: 10.1111/sji.12649. Review. PMID: 29476557
It is essential to know the pathways of pathogenesis and the key cytokines involved in any disease before the targets of therapy are identified. In the quest for new molecular targets in Sjögren’s syndrome, Zhang et al. conducted a meta-analysis of articles exploring the role of IL-17 in SS. They concluded that the expression of IL-17 is significantly increased in patients with SS, especially those without receiving any immunosuppressive therapy, compared to controls. In addition, patients with SS with positive rheumatoid factor (RF) tend to express a higher level of IL-17 than patients without RF. Furthermore, the IL-17 level correlates with the disease severity of SS, especially ocular symptoms. These findings demonstrate the significance of IL-17 overexpression in patients with SS and may provide insights for targeting IL-17 as a therapeutic option for SS.
3. Combined interventional sialendoscopy and intraductal steroid therapy for recurrent sialadenitis in Sjögren's syndrome: Results of a pilot monocentric trial. Capaccio P, Canzi P, Torretta S, Rossi V, Benazzo M, Bossi A, Vitali C, Cavagna L, Pignataro L. Clin Otolaryngol. 2018 Feb;43(1):96-102. doi: 10.1111/coa.12911. Epub 2017 Jun 26. PMID: 28585263
There are limited options when it comes to treating a patient with Sjögren’s syndrome. There is an ongoing quest for any new molecules or any other modalities of treatment. Capaccio et al. in their recent trial evaluated whether interventional sialendoscopy and intraductal steroid therapy could make any difference in the management of Sjögren’s syndrome. In group A (n=12), patients underwent both sialendoscopy and intraductal steroid irrigation, and in group B (n=10), patients underwent only sialendoscopy. Both groups were followed up for six months. The postoperative reduction in the mean number of episodes of glandular swelling was 87% (95% CI: 77–93) and 75% (95% CI: 47%–88%) in the groups A and B, respectively. The percentage of patients with glandular swelling decreased from 41.7% to 0.0% in group A and from 30.0% to 0.0% in group B, respectively. Most patients experienced a subjective clinical improvement, documented by the statistically significant reduction in the postoperative mean pain VAS (group A p<0.001; group B p=0.004), Xerostomia Inventory (p<0.001 and p=0.003), and ESSPRI scores (p<0.001 and p=0.008). Interventional sialendoscopy followed by outpatient intraductal steroid irrigations was more effective than interventional sialendoscopy alone, when pain VAS, Xerostomia Inventory, and ESSPRI scores before and after treatment were analyzed together using the multivariate Hotelling T2 test (p=0.0173). However, the study has limitations: it was a single-center study and lacked a control group; this might have allowed for bias. Larger multicenter studies are required to establish whether this experimental modality can help alleviate symptoms of Sjögren’s syndrome.

Dr. Saumya Ranjan Tripathy, MD, DM
Assistant Professor, Department of Rheumatology, SCBMCH, Cuttack
Landmark Papers in Vasculitides: 2018
During the year 2018, there were almost 2500 PubMed indexed publications in the medical field of vasculitis. A concise summary of a few relevant and interesting papers is presented below:
1. Sunderko ̈tter CH, Zelger B, Chen KR, et al. Nomenclature of cutaneous & vasculitis: dermatologic addendum to the 2012 revised international Chapel Hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018; 70:171–184.
Sunderkotter et al. on behalf of Chapel Hill Consensus Conference (CHCC) have proposed an addendum to the CHCC 2012 that focuses on the nomenclature of cutaneous vasculitis. CHCC 2012 had not dealt with the special features of cutaneous vasculitis and had not clearly discussed the presence of skin-limited or skin-dominant forms of vasculitis. The goal of this addendum is to standardize names and definitions for cutaneous vasculitis, but not to establish diagnostic criteria. The authors have defined five new terms: cutaneous IgM/IgG immune complex vasculitis, nodular cutaneous vasculitis (erythema induratum of Bazin), erythema elevatum et diutinum, recurrent macular vasculitis in hypergammaglobulinemia (hypergammaglobulinemic purpura of Waldenstrom), and normocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis (NUV) (non–anti-C1q vasculitis). The authors have also clearly defined vasculitis associated with systemic disease as vasculitis that is associated with and may be secondary to or caused by a systemic disease (e.g. rheumatoid vasculitis, SLE, sarcoid vasculitis, etc.). They suggest that name (diagnosis) should have a prefix specifying the systemic disease (e.g. rheumatoid vasculitis, lupus vasculitis, etc.). In these disorders, the type of cutaneous vasculitis (small vessel or medium vessel vasculitis) varies depending on the underlying systemic disease. Additionally, when the cutaneous vasculitis occurs without systemic vasculitis (the name should be, e.g. skin-limited rheumatoid vasculitis, etc.). Single organ vasculitis is defined as vasculitis in a single organ that has no features, and indicates that it is a limited expression of systemic vasculitis. Also, the CHCC addendum has recognized cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa as a distinct subtype of polyarteritis nodosa.
2. Peter CVD, Pulimood A S, George L et al., Clinicopathological study on rickettsial spotted fever from south India. Trop Doct 2018 Oct;48(4):325-329. doi:10.1177/0049475518794580.
This interesting and clinically relevant study is published from CMC Vellore. Tick-borne Rocky Mountain spotted fever typically presents with generalized purpuric rash, which frequently involves the palms and soles, fever, and arthralgia/arthritis. The authors performed a biopsy of the skin lesions, as clinical manifestations closely mimic systemic vasculitis. Histopathology revealed vasculitis with a mixed inflammatory infiltrate in about half of the patients. Apart from the predominant small vessel vasculitis, a small proportion of the biopsies (11%) also showed a medium vessel vasculitis. Thus, Rickettsia infections must be considered in a febrile patient with vasculitic purpuric rash even if the skin bio psy shows features favoring small vessel vasculitis.
3. Wang K, Sun X, Cao YD etal. Risk factors for renal involvement and severe kidney disease in 2731 Chinese children with Henoch Schönlein purpura: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(38): doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012520.
Wang et al. conducted a retrospective study to identify risk factors for developing renal involvement and severe kidney disease in Chinese childhood Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) patients. This study was conducted among 2731 children with HSP diagnosed between 2012 and 2015. They used multivariate logistic regression analysis to assess the risk factors. Renal involvement occurred in 844 HSP patients (35.60%), and severe kidney disease occurred in 104 HSP patients (4.39%). Age over six years old at onset, colder season, more than eight days’ interval between symptom onset and diagnosis, residence in rural areas, recurrence, angioedema, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement were significant risk factors for renal involvement. At the same time, age over six years at onset, more than eight days’ interval between symptom onset and diagnosis, recurrence, angioedema, and CNS involvement were highly associated with severe kidney disease. Angioedema, a longer interval between symptom onset and diagnosis, older age at HSP onset, and recurrence are prognostic indicators for renal involvement and severe kidney disease in children with HSP.
4. i) Conway R, O'Neill L, Gallagher P etal, Ustekinumab for refractory giant cell arteritis: A prospective 52-week trial. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018 Dec;48(3):523-528. doi: 10. 1016/j. semarthrit. 2018. 04.004.
Several important publication were made in large vessel vasculitis in 2018. A prospective open-label study on ustekinumab in patients with 25 refractory GCA was reported by Conway et al. Ustekinumab 90 mg was administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks. All patients had failed to taper glucocorticoids despite the addition of a median of one other immunosuppressive agent. The primary outcome was the comparison of the median glucocorticoid dose prior to the commencement of ustekinumab and at 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes included physician-assessed relapse, acute-phase reactants, and imaging assessment of large vessel vasculitis (LVV). At week 52, median (IQR) daily prednisolone dose decreased from 20 (15, 25)mg to 5 (2.5, 5) mg (p<0.001). Six patients (24%) stopped prednisolone completely. No patient experienced a relapse of GCA while receiving ustekinumab. CT angiography demonstrated improvement of LVV in all patients studied. No unexpected AEs were observed with ustekinumab. The authors concluded that ustekinumab may be effective for the treatment of GCA and warrants further assessment in a randomized controlled trial.
ii) Leon L, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Morado I, etal.Treatment with methotrexate and risk of relapses in patients with giant cell arteritis in clinical practice. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018 Mar-Apr;36 Suppl 111(2): 121-128.
The utility of methotrexate in preventing relapse in GCA was tested by a Spanish group. An inception cohort of 168 GCA patients (675 patient-years) was assembled, including patients from the date of diagnosis (Jan 1991–Sept 2013), and followed up until lost of follow-up or Sept 2014. Thirty-one percent of patients relapsed. In the multivariate analysis, exposure to MTX had a 72% lower risk of relapse compared to those without MTX (p<0.05). The authors concluded that use of MTX seems to decrease the risk of recurrences.
iii) Goel R, Danda D, Joseph G etal. Long-term outcome of 251 patients with Takayasu arteritis on combination immunosuppressant therapy: Single centre experience from a large tertiary care teaching hospital in Southern India. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018 Apr;47(5):718-726. doi: 10.1016/j. semarthrit.2017.09.014.
The utility of methotrexate in preventing relapse in GCA was tested by a Spanish group. An inception cohort of 168 GCA patients (675 patient-years) was assembled, including patients from the date of diagnosis (Jan 1991–Sept 2013), and followed up until lost of follow-up or Sept 2014. Thirty-one percent of patients relapsed. In the multivariate analysis, exposure to MTX had a 72% lower risk of relapse compared to those without MTX (p<0.05). The authors concluded that use of MTX seems to decrease the risk of recurrences.
IV) Grayson PC, Alehashemi S, Bagheri AA et al. 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography As an Imaging Biomarker in a Prospective, Longitudinal Cohort of Patients With Large Vessel Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Mar;70(3):439-449. doi: 10.1002/art.40379. Epub 2018 Feb 6.
The clinical value of FDG-PET in LVV was explored by Grayson et al. A qualitative summary score based on global arterial FDG uptake and the PET Vascular Activity Score (PETVAS) was used to study associations between activity on PET scan and clinical characteristics and to predict relapse. FDG-PET distinguished patients with clinically active LVV from comparator subjects with a sensitivity of 85% (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 69, 94) and a specificity of 83% (95% CI 71, 91). FDG-PET scans were interpreted as active vasculitis in most patients with LVV in clinical remission (41 of 71 [58%]). Among patients who underwent PET during clinical remission, future clinical relapse was more common among patients with a high PETVAS vs. those with a low PETVAS (55% vs. 11%; p=0.03) over a median follow-up period of 15 months.
v) Dejaco C, Ramiro S, Duftner C et al EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice.,Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 May;77(5):636-643. doi: 10.1136/ annrheumdis -2017-212649. Epub 2018 Jan 22.
Evidence-based recommendations were published by EULAR for the use of imaging in LVV. An early imaging test is recommended in patients with suspected LVV, with ultrasound and MRI being the first choices in GCA and TAK, respectively. CT or PET may be used alternatively. In case the diagnosis is still uncertain after clinical examination and imaging, additional investigations, including temporal artery biopsy and/or additional imaging, are required. In patients with a suspected flare, imaging might help to better assess disease activity.
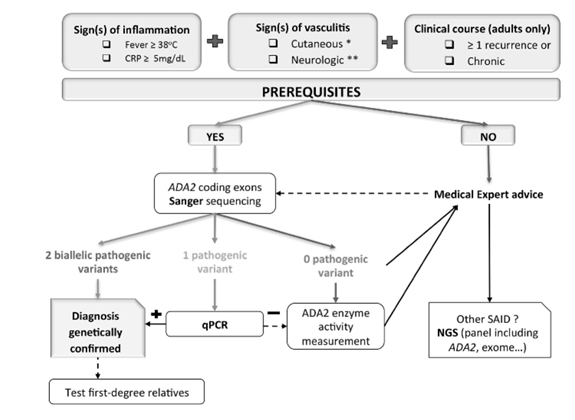
5. Mélanie Rama, Claire Duflos, Isabelle Melki etal, A decision tree for the genetic diagnosis of deficiency of adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2): a French reference centres experience, European Journal of Human Genetics (2018) 26:960–971 https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s 41431-018-0130-6 Rama et al.
on behalf of a French group have proposed a decision tree that may help improve obtaining genetic confirmation of DADA2 in the context of autoinflammatory symptoms. This is based on their experience of genetic analysis of 66 patients with clinically suspected DADA2. Prerequisites for quick and low-cost Sanger analysis include one typical cutaneous or neurological sign, one marker of inflammation (fever or elevated CRP level), and recurrent or chronic attacks in adults.
6. Baulier G, Issa N, Gabriel F, etal. Guidelines for prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia cannot rely solely on CD4-cell count in autoimmune and inf lammatory diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):490-493.
In this interesting paper by Baulier G et al., the authors retrospectively studied CD4 and lymphocyte-count in 129 patients diagnosed with PCP between January 2013 and February 2016. They found that the median CD4 count was 302/mm3 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, which was significantly higher than that in HIV patients (19/mm3; p<0.0001). Fifty percent (n=10) of patients had CD4 counts higher than 300/mm3. The authors concluded that prophylaxis for PCP cannot rely solely on CD4 count in non-HIV patients, especially in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
7. Few publications on ANCA vasculitis deserve a mention
Sharma A, Naidu GSRSNK, Rathi M et al. Clinical features and long-term outcomes of 105 granulomatosis with polyangiitis patients: A single center experience from north India. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018 Jan;21(1):278-284. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13071
Shobha V, Fathima S, Prakash R. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: clinical course and outcome of 60 patients from a single center in South India. Clin Exp Med. 2018 Aug;18(3):347-353. doi: 10.1007/s10238-018-0492-7.
Two centers in India reported their experience in granulomatosis and polyangiitis in 2018. These two series are the largest series of GPA reported from India. Sharma et al. described the clinical features and outcomes in 105 patients and Shobha et al. in 60 patients of GPA. Renal involvement was seen in 51% of patients in the series from North India and in 70% of patients from South India. Both series noted high disease activity with high BVAS at presentation. The mortality was mainly due to disease activity and seen in 17% in the series by Sharma et al. and in 15% by Shobha et al. Most patients were treated with cyclophosphamide in both series. Relapses were reported in 26/105 patients by Sharma et al. The outcomes are mortality reported by the two centers are comparable to other large reported series of GPA.
Terrier B, Pagnoux C, Perrodeau É et al.Long-term efficacy of remission-maintenance regimens for ANCA-associated vasculitides. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Aug;77(8):1150-1156. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212768
The French vasculitis group reported 60-month follow-up data from the MAINRITSAN trail comparing rituximab and azathioprine for maintenance in ANCA vasculitis. For the azathioprine and rituximab groups, respectively, at month 60, the major relapse-free survival rates were 49.4% (95% CI 38.0% to 64.3%) and 71.9% (95% CI 61.2% to 84.6%) (p=0.003); minor and major relapse-free survival rates were 37.2% (95% CI 26.5% to 52.2%) and 57.9% (95% CI 46.4% to 72.2%) (p=0.012); overall survival rates were 93.0% (95% CI 86.7% to 99.9%) and 100% (p=0.045) and cumulative glucocorticoid use was comparable. Rituximab was superior to azathioprine at month 60.

Dr. Benzeeta Pinto, Asst. Prof., Dept. of Clinical Immunology & Rheumatology,
St. John’s Med College, Bangalore
Compiled by

Dr. Taral Parikh, Rheumatologist, Ahmedabad












